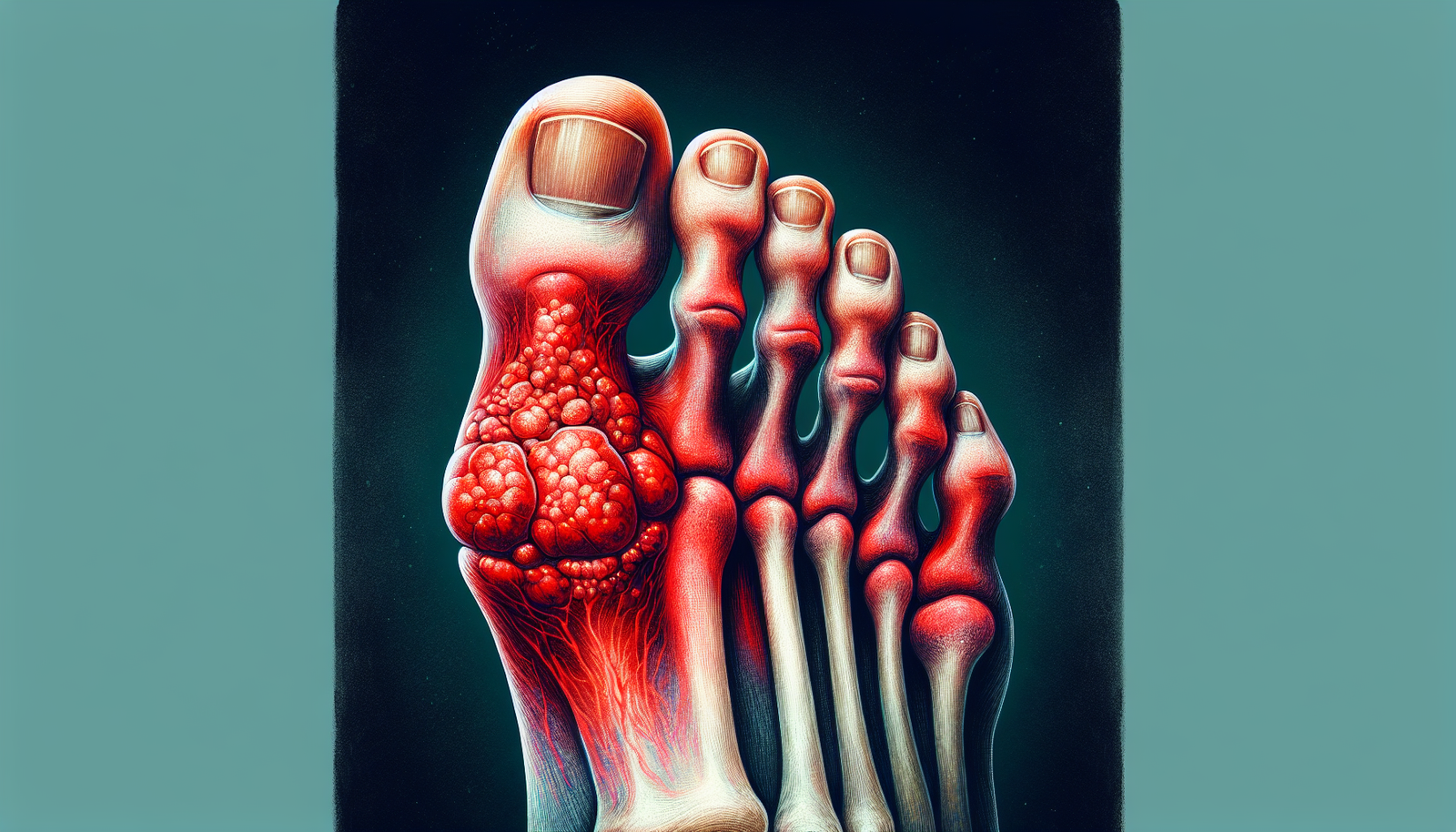
Sure, you've probably heard of gout before, but do you really know what it entails? Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs when there is an excessive buildup of uric acid in your body. This buildup can lead to the formation of tiny crystals in your joints, causing intense pain and discomfort. So, let's talk about the symptoms of gout and how you can recognize them. Gout is a form of arthritis that is characterized by sudden and intense pain, swelling, and tenderness in the joints. It is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, which leads to inflammation and pain. Gout can affect anyone, but it is more common in men and women after menopause. In this article, we will explore the various symptoms of gout and how they can vary depending on the duration of the condition and the joints affected.

Acute Gout Symptoms
Severe joint pain
One of the most noticeable symptoms of gout is severe joint pain. This pain typically occurs suddenly and is often described as throbbing or excruciating. The joints most commonly affected by gout are the big toe, ankle, knee, wrist, fingers, and elbow. The pain can be so intense that even the slightest touch or movement is excruciating.
Swelling and redness
In addition to severe joint pain, gout can also cause swelling and redness in the affected joint. The joint may appear larger than usual and feel hot to the touch. This swelling and redness are a result of the inflammation caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals.
Warmth and tenderness
Another symptom of gout is warmth and tenderness in the joint. The affected area may feel warm to the touch and be sensitive to pressure. This tenderness can make it difficult to perform normal daily activities, such as walking or using your hands.
Limited range of motion
Gout can also lead to limited range of motion in the affected joint. The inflammation and pain can make it challenging to move the joint fully, leading to stiffness and decreased flexibility. This limitation in movement can further impact your ability to carry out everyday tasks.
Chronic Gout Symptoms
Recurrent gout attacks
Chronic gout refers to the condition where gout attacks occur frequently or persistently. Instead of experiencing isolated episodes of gout, those with chronic gout may find themselves dealing with recurrent flare-ups over an extended period. The frequency and intensity of these attacks can vary from person to person.
Persistent joint discomfort
Along with recurrent gout attacks, individuals with chronic gout often experience persistent joint discomfort. The affected joint may not return to its normal state completely between flare-ups, resulting in an ongoing sense of uneasiness or discomfort. This can greatly impact a person's quality of life and ability to perform everyday activities.
Formation of tophi
Tophi are small, uric acid crystal deposits that can form under the skin. These tophi typically develop in areas where gout attacks occur, such as the fingers, elbows, or toes. Tophi may appear as visible lumps or nodules that can be yellowish or whitish in color. They can range in size and texture, from soft and squishy to hard and firm.
Pain or tenderness in tophi
Having tophi can also result in pain or tenderness in the affected area. As the tophi grow, they can put pressure on surrounding tissues, causing discomfort. Moreover, the presence of tophi can make the joints more susceptible to inflammation and gout attacks.
Complications of Gout
Joint damage
If left untreated or poorly managed, gout can lead to joint damage. Persistent inflammation in the joints can cause erosion of cartilage and bone, resulting in joint deformities and reduced joint function. Over time, this can significantly impact a person's mobility and ability to perform daily activities.
Kidney stones
Gout is associated with an increased risk of developing kidney stones. These stones are formed by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the urinary tract. Kidney stones can cause severe pain and discomfort and may require medical intervention, such as medication or surgical procedures, for removal.
Uric acid kidney stones
Uric acid kidney stones are a specific type of kidney stone caused by high levels of uric acid in the urine. These stones can form when there is an excess of uric acid in the body, which is commonly seen in individuals with gout. Uric acid kidney stones can cause renal colic, a type of severe pain that radiates from the back to the lower abdomen.
Kidney damage
In some cases, gout can lead to kidney damage. The accumulation of uric acid crystals in the kidneys can cause inflammation and impair kidney function over time. This damage can result in chronic kidney disease or even kidney failure if left untreated.
Gout Symptoms in Different Joints
Gout can affect various joints in the body, each presenting its own unique set of symptoms. Let's take a closer look at the symptoms of gout in different joints:
Symptoms in the big toe
Gout attacks in the big toe, also known as podagra, are quite common. Symptoms in this joint include severe pain, swelling, redness, and limited mobility. The intense pain experienced in the big toe during a gout attack often makes it difficult to walk or wear shoes.
Symptoms in the ankle
Gout can also affect the ankle joint, leading to similar symptoms as seen in the big toe. The ankle may become swollen, red, and tender to the touch. Walking or putting weight on the affected ankle can elicit severe pain.
Symptoms in the knee
When gout affects the knee joint, symptoms may include pain, swelling, and redness. The knee can feel warm to the touch, and the range of motion may be limited. This can result in difficulty walking, bending, or fully extending the leg.
Symptoms in the wrist
In some cases, gout can target the wrist joint, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility. The wrist may appear red and feel warm to the touch. The discomfort can make it challenging to perform activities that involve wrist movement, such as writing or lifting objects.
Symptoms in the fingers
Gout attacks in the fingers can lead to pain, swelling, and tenderness. The finger joint may be visibly swollen and red. These symptoms can make it difficult to perform fine motor tasks, such as typing or gripping objects.
Symptoms in the elbow
Gout can also affect the elbow joint, causing pain, swelling, and tenderness. The elbow may become red and warm to the touch. Movements that involve bending or extending the arm can be particularly painful during a gout flare-up.
Gout Flare-Up Symptoms
Sudden and intense pain
During a gout flare-up, the pain is often sudden and intense. It can come on without warning and escalate rapidly. The excruciating pain typically reaches its peak within the first 24 hours and gradually subsides over the course of several days to weeks.
Rapid onset of symptoms
Gout flare-ups can have a rapid onset, with symptoms appearing suddenly and escalating quickly. One moment you may be feeling normal, and the next you can experience severe joint pain, swelling, and redness. This rapid onset can be alarming and disruptive to your daily routine.
Severe redness and swelling
During a flare-up, the affected joint may become severely red and swollen. The joint can appear larger than usual, and the skin covering the joint may feel tight or stretched. The redness and swelling are signs of inflammation caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals.
Warmth and tenderness in the affected joint
An inflamed joint during a gout flare-up is often warm to the touch and tender. The warmth can be detected by comparing the affected joint to a neighboring joint or to the corresponding joint on the other side of the body. The tenderness can make even the lightest touch painful and uncomfortable.
Gout Symptoms in Women
Location of gout attacks
Although gout is more common in men, women can also experience gout attacks. When women develop gout, they tend to have a higher frequency of attacks in the lower extremities, such as the ankles and knees. Gout attacks in women may also occur in the fingers and wrists.
Timing of gout attacks
In women, gout attacks can be influenced by hormonal changes throughout the menstrual cycle. Some women may experience more frequent gout attacks during or just before their periods, while others may notice an increase in symptoms during menopause. These hormonal fluctuations can impact uric acid levels and trigger gout attacks.

Gout Symptoms in Men
Common areas affected by gout
Gout attacks in men most commonly affect the big toe joint, a condition known as podagra. However, gout can also affect other joints such as the ankles, knees, elbows, and wrists. Men may experience gout attacks in multiple joints simultaneously or at different times.
Relation to age and hormones
The risk of developing gout increases as men age, with the condition typically becoming more prevalent in middle-aged and older men. Hormonal factors can also play a role in triggering gout attacks in men. High levels of testosterone and low levels of estrogen have been associated with an increased risk of developing gout.
Non-Joint Gout Symptoms
Kidney symptoms
Alongside joint symptoms, gout can also lead to various kidney-related symptoms. These symptoms may include blood in the urine, frequent urination, pain or discomfort in the kidney area, and changes in urine color or consistency. If you experience any kidney-related symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Uric acid buildup in soft tissues
In addition to the joints and kidneys, uric acid crystals can accumulate in soft tissues, causing symptoms such as the formation of tophi under the skin. These tophi can develop in areas such as the fingers, elbows, or ears, and may lead to pain, tenderness, and visible lumps under the skin.
In conclusion, gout is a painful and potentially debilitating condition characterized by various symptoms. Whether it is acute or chronic gout, recognizing the signs and symptoms is crucial for proper management and treatment. Gout can affect different joints in the body, with each joint presenting its own unique set of symptoms. Additionally, gout can lead to complications such as joint damage and kidney stones. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of gout to receive a proper diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan to alleviate pain and prevent further complications.